
The spleen is an organ found in all vertebrate animals. In humans, the spleen is located in the abdomen of the body, where it functions in the destruction of redundant red blood cells, and holds a reservoir of blood. It is one of the centers of activity of the reticuloendothelial system (part of the immune system). Its absence leads to a predisposition to certain infections.
 (Enlarged view of spleen)
(Enlarged view of spleen)Anatomy
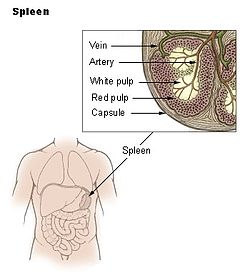
The spleen is an organ found in the left upper abdomen above the stomach and underneath the rib cage. Spleens in healthy adult humans are approximately 9 to 13 centimetres (3 to 5 in) in length.
Like the thymus, the spleen possesses only efferent lymphatic vessels.
Function
Area (Function)
| Spleen | |
|---|---|
Red pulp (Mechanical filtration. Removes
unwanted materials from the blood,
including old red blood cells)
White pulp ( Helps fight infections)
Functions of the spleen are less prominent, especially in the healthy adult:
- Production of opsonins, properdin, and tuftsin.
- Creation of red blood cells. While the bone marrow is the primary site of hematopoeisis in the adult, the spleen has important hematopoietic functions up until the fifth month of gestation. After birth, erythropoietic functions cease except in some hematologic disorders. As a major lymphoid organ and a central player in the reticuloendothelial system the spleen retains the ability to produce lymphocytes and, as such, remains an hematopoietic organ.
- Storage of red blood cells and other formed elements. This is only valid for certain mammals, such as dogs and horses. In horses roughly 50% of the red blood cells are stored there. The red blood cells can be released when needed These animals also have large hearts in relation to their body size to accommodate the higher-viscosity blood that results. In humans, however, the spleen does not function as a depository of red blood cells, but instead it stores platelets in case of an emergency. Some athletes have tried doping themselves with their own stored red blood cells to try to achieve the same effect, but the human heart is not equipped to handle the higher-viscosity blood.
Disorders
Disorders include splenomegaly, where the spleen is enlarged by various reasons. On the other hand, a lack of normal spleen function is called asplenia.











No comments:
Post a Comment