 (Representation of Human Respiratory Tract.)
(Representation of Human Respiratory Tract.)Respiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.
Volumes
- lung volumes
- vital capacity
- functional residual capacity
- dead space
- spirometry
- body plethysmography
- peak flow meter
Mechanics
Breathing in, or inhaling, is usually an active movement. The contraction of the diaphragm muscles cause a pressure variation, which is equal to the pressures caused by elastic, resistive and inertial components of the respiratory system.
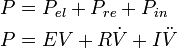
Where Pel equals the product of elastance E (inverse of compliance) and volume of the system V, Pre equals the product of flow resistance R and time derivate of volume V (which is equivalent to the flow), Pin equals the product of inertance I and second time derivate of V. R and I are sometimes referred to as Rohrer's constants.
- Anatomy: pleural cavity, thoracic diaphragm, Intercostales externi muscles, Intercostales interni muscles
- inhalation and exhalation
- lung, pulmonary alveolus
- With insufficient pulmonary surfactant, the pulmonary alveoli collapse, causing atelectasis (in infants, infant respiratory distress syndrome)
- the law of Laplace,
- compliance (physiology) - decreased with fibrosis, increased with emphysema
- Poiseuille's law
- asthma and COPD
- hysteresivity
Circulation, ventilation, and perfusion
- pulmonary circulation
- positive pressure ventilation
- hypoxic vasoconstriction
- ventilation (physiology), perfusion, ventilation/perfusion ratio (V/Q), and ventilation/perfusion scan
- shunts: right-to-left (tetralogy of fallot), left-to-right (patent ductus arteriosus)
- respiratory rate and respirometer
Gas exchange/transport (primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide)
- gas exchange
- Dalton's law
- hemoglobin
- oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve, Bohr effect, Haldane effect
- carbonic anhydrase
- oxyhemoglobin
- respiratory quotient
- arterial blood gas
Control and response
- control of respiration
- reticular formation
- pons (apneuistic and pneumotaxic)
- chemoreceptors (medulla, carotid body, aortic body)
- Hering-Breuer reflex
- involuntary control of respiration
- exercise
- hyperoxia
- hypoxemia (hypoxic hypoxia)
Disorders
- altitude sickness
- asthma
- carbon monoxide poisoning
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- emphysema
- infant respiratory distress syndrome
- pulmonary edema














No comments:
Post a Comment