
In anatomy of the digestive system, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25-30 cm (10-12 in) long connecting the stomach to the jejunum. It is the first and shortest part of the small intestine where most chemical digestion takes place. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the ligament of Treitz. The name duodenum is from the Latin duodenum digitorum, twelve fingers' breadths.
Function
The duodenum is largely responsible for the breakdown of food in the small intestine. Brunner's glands, which secrete mucus, are found in the duodenum. The duodenum wall is composed of a very thin layer of cells that form the muscularis mucosae. The duodenum is almost entirely retroperitoneal.
The duodenum also regulates the rate of emptying of the stomach via hormonal pathways. Secretin and cholecystokinin are released from cells in the duodenal epithelium in response to acidic and fatty stimuli present there when the pyloris opens and releases gastric chyme into the duodenum for further digestion. These cause the liver and gall bladder to release bile, and the pancreas to release bicarbonate and digestive enzymes such as trypsin, lipase and amylase into the duodenum as they are needed.
New studies have shown that around 80% of obese people who had gastric bypass surgery (bypassing the duodenum) were cured of their Type 2 Diabetes. However, the disappearance of their diabetes came long before the actual weight loss. When the same operation was performed on diabetic rats, they too were rid of their diabetes. However, when the operation was reversed in the animals, the diabetes returned. This shows that preventing food from entering the duodenum can have a dramatic impact on people suffering from Type 2 Diabetes.
Sections
The duodenum is divided into four sections for the purposes of description. The first three sections form a "C" shape.
First part
The first (superior) part begins as a continuation of the duodenal end of the pylorus. From here it passes laterally (right), superiorly and posteriorly, for approximately 5 cm, before making a sharp curve inferiorly into the superior duodenal flexure (the end of the superior part). It is intraperitoneal.
Second part
The second (descending) part of the duodenum begins at the superior duodenal flexure. It passes inferiorly to the lower border of vertebral body L3, before making a sharp turn medially into the inferior duodenal flexure (the end of the descending part).
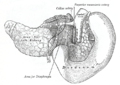
The pancreatic duct and common bile duct enter the descending duodenum, commonly known together as the hepatopancreatic duct (or pancreatic duct in the United States), through the major duodenal papilla. This part of the duodenum also contains the minor duodenal papilla, the entrance for the accessory pancreatic duct. The junction between the embryological foregut and midgut lies just below the major duodenal papilla.
Third part
The third (inferior/horizontal) part of the duodenum begins at the inferior duodenal flexure and passes transversely to the left, crossing the inferior vena cava, aorta and the vertebral column.
Fourth part
The fourth (ascending) part passes superiorly, either anterior to, or to the right of, the aorta, until it reaches the inferior border of the body of the pancreas. Then, it curves anteriorly and terminates at the duodenojejunal flexure where it joins the jejunum. The duodenojejunal flexure is surrounded by a peritoneal fold containing muscle fibres: the ligament of Treitz.
Blood Supply
The duodenum receives arterial blood from two different sources. The transition between these sources is important as it determines the foregut from the midgut. Proximal to the 2nd part of the duodenum (approximately at the major duodenal papilla - where the bile duct enters) the arterial supply is from the gastroduodenal artery and its branch the superior pancreatoduodenal artery. Distal to this point (the midgut) the arterial supply is from the superior mesenteric artery, and its branch the inferior pancreatoduodenal artery supplies the 3rd and 4th sections. The superior and inferior pancreatoduodenal arteries (from the gastroduodenal artery and SMA respectively) form an anastomotic loop between the celiac trunk and the SMA; so there is potential for collateral circulation here.
The venous drainage of the duodenum follows the arteries. Ultimately these veins drain into the portal system, either directly or indirectly through the splenic or superior mesenteric vein.
Lymphatic Drainage
The lymphatic vessels follow the arteries in a retrograde fashion. The anterior lymphatic vessels drain into the pancreatoduodenal lymph nodes located along the superior and inferior pancreatoduodenal arteries and then into the pyloric lymph nodes (along the gastroduodenal artery). The posterior lymphatic vessels pass posterior to the head of the pancreas and drain into the superior mesenteric lymph nodes. Efferent lymphatic vessels from the duodenal lymph nodes ultimately pass into the celiac lymph nodes.




















No comments:
Post a Comment